Ōita Prefecture
Guideto Japan
Culture History- English
- 日本語
- 简体字
- 繁體字
- Français
- Español
- العربية
- Русский
Ōita Prefecture is located in northeast Kyūshū. It borders Fukuoka, Kumamoto, and Miyazaki Prefectures and faces the Seto Inland Sea and Bungo Strait. Largely mountainous, the prefecture has huge tracts of forested land as well as a long, rugged coastline that includes features like Beppu Bay, where the capital and other population centers are clustered, and remote headlands.
Ōita Prefecture at a Glance
- Established in 1871 (formerly Bungo province)
- Capital: Ōita
- Population: 1,124,000 (as of Oct. 2020)
- Area: 6,341 km2
Ōita has an abundance of hot springs, including the famed onsen resorts of Beppu and Yufuin. Large swaths of the prefecture fall within the boundaries of Aso-Kujū National Park, offering visitors scenic views and outdoor activities. The town of Usuki on the coast is known for its ancient stone Buddhas and the remote Kunisaki Peninsula on the northeast coast features historic temples and shrines, including 1,300-year old Usa Jingū, set among the natural beauty of Mount Futago.
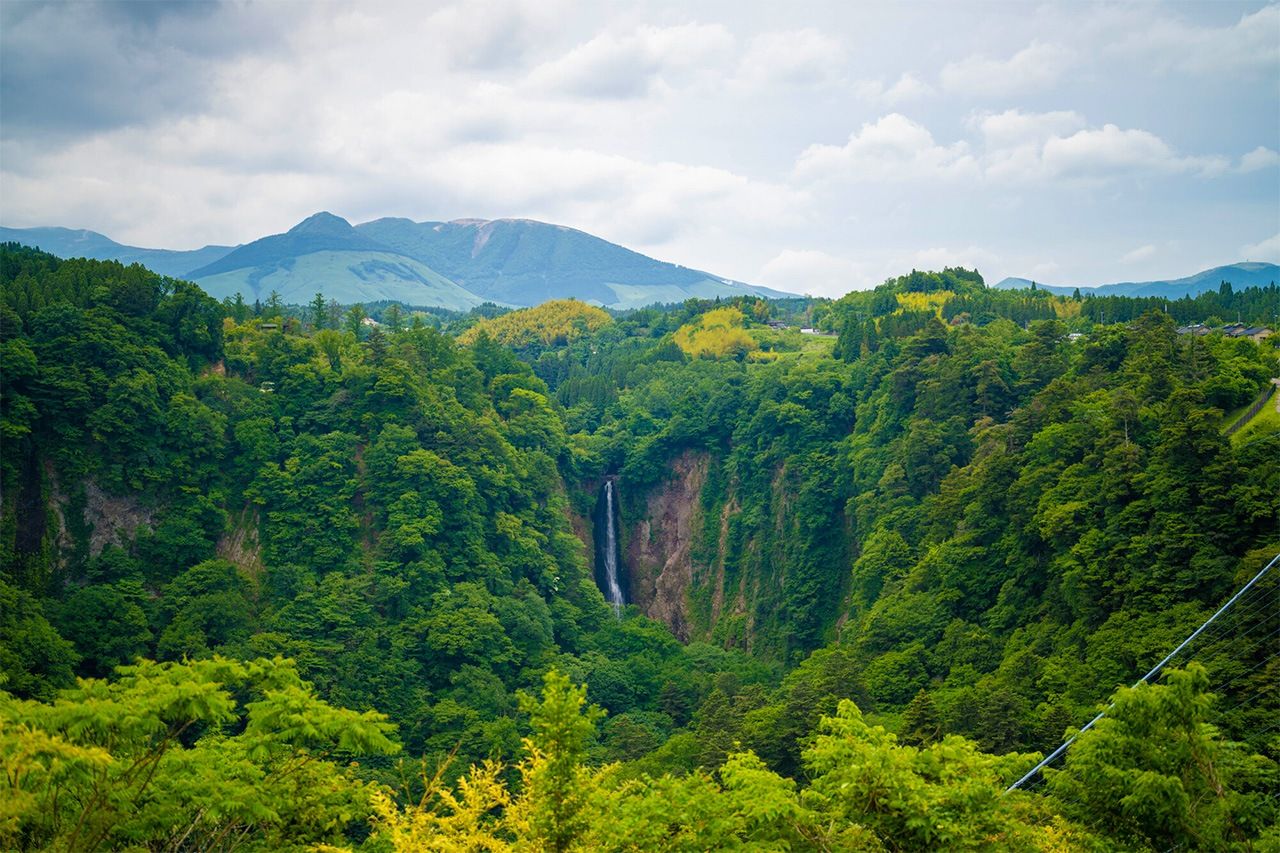

Shindō Falls in the Kujū mountains. (© Pixta)
Ōita has a large agricultural sector centered on the production of rice and staple vegetables, with the prefecture being known for the citrus fruit kabosu and wagyū cattle. Forestry is a core industry, and the rich fisheries bring in catches of sardines and mackerel along with farmed yellowtail and flounder. Manufacturing output includes the production of transportation equipment, metals, and industrial chemicals.
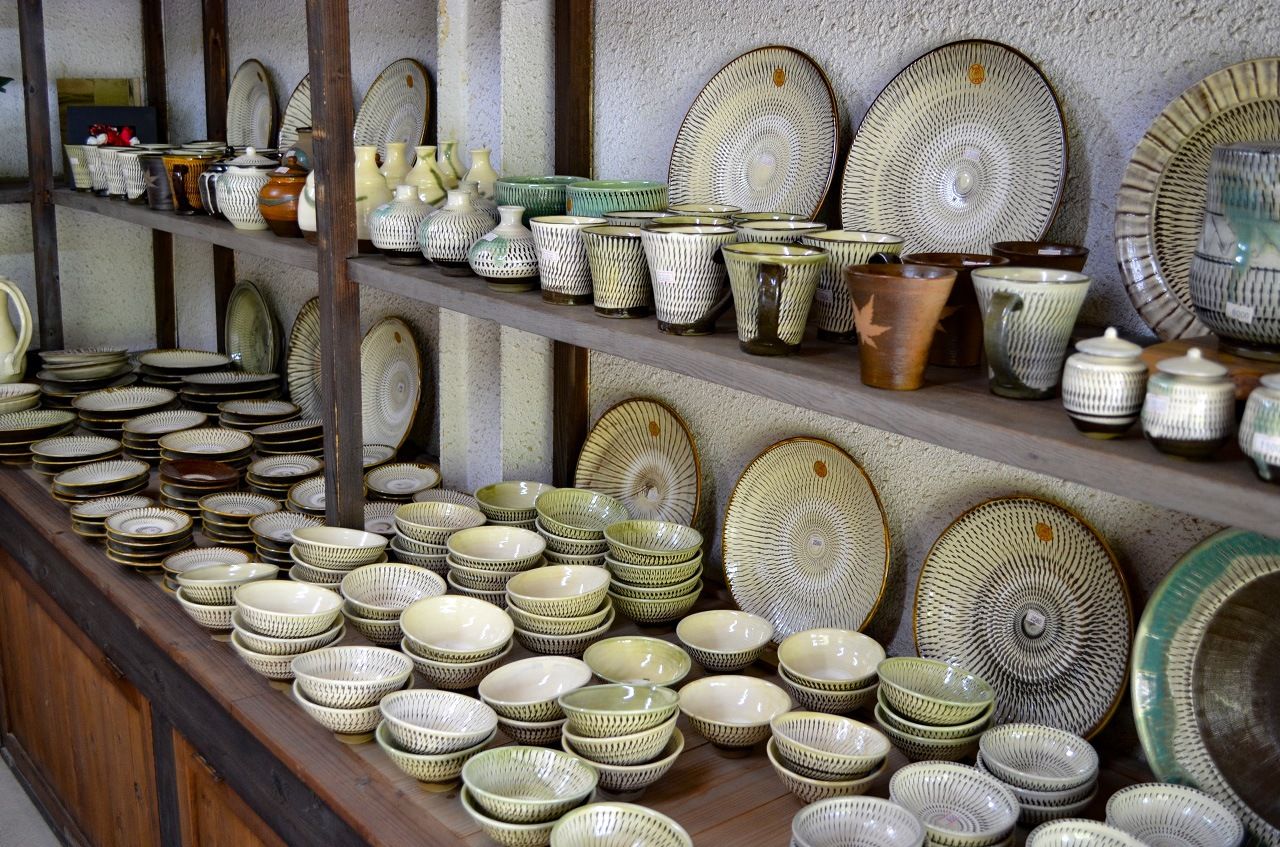

Pieces of Ontayaki pottery. The distinctly designed earthenware tradition is designated an intangible cultural property. (© Pixta)

Ōita’s official mascot Mejiron is modeled on the prefectural bird, the mejiro, or Japanese white-eye. (© Ōita Prefecture #1483)
Famous Figures
- Fukuzawa Yukichi (1835–1901): Educator and entrepreneur. Was part of Japan’s first missions to the United States in 1860 and Europe in 1862. Founded Keiō University and the influential newspaper Jiji Shinpō.
- Nogami Yaeko (1885–1985): Novelist who studied under Natsume Sōseki. Author of Meiro (trans. The Labyrinth) and Hideyoshi to Rikyū (trans. Hideyoshi and Rikyū).
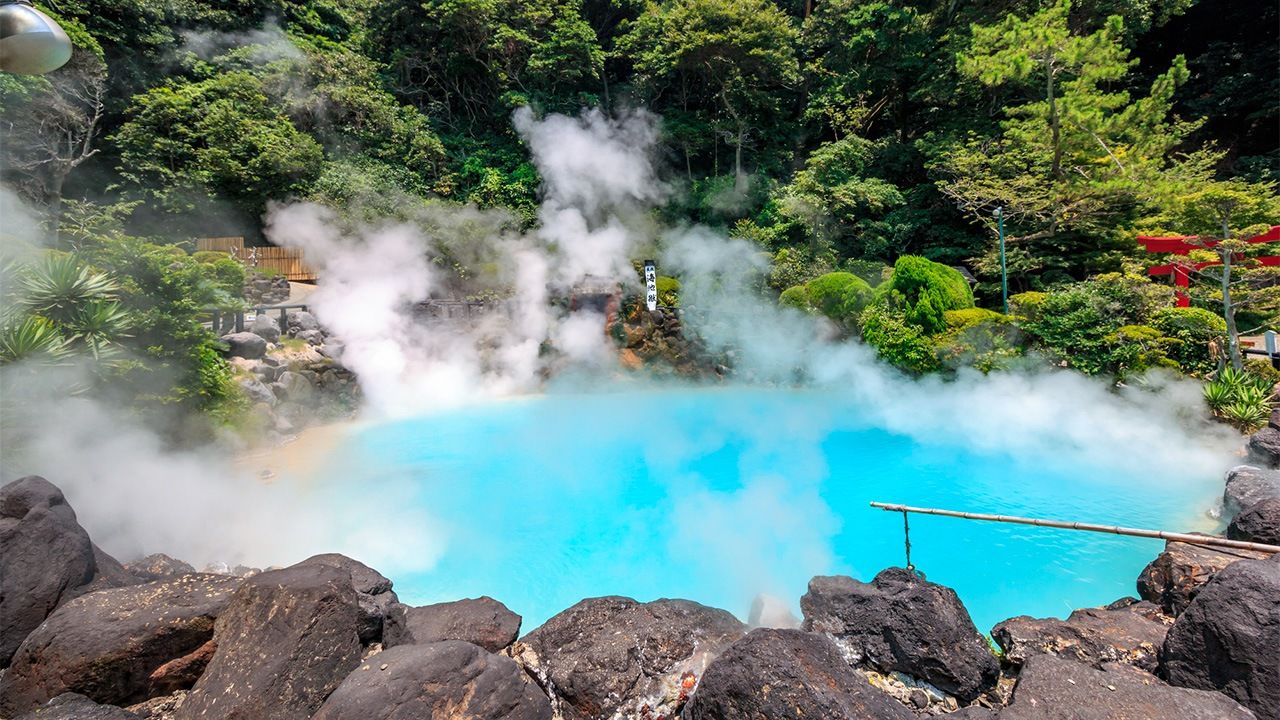
(Originally published in English. Banner photo: The steaming waters of Beppu Onsen’s Umijigoku. © Pixta.)
For the complete list of the country’s 47 prefectures, see “The Prefectures of Japan.”